Pneumatic air cylinders are crucial in various industrial applications to create linear motion using compressed air. It’s important to calculate the force of pneumatic air cylinders accurately to ensure that these cylinders perform effectively.
This blog will guide you through the methods for calculating the force of pneumatic air cylinders, specifically focusing on how to use a calculator for these calculations.
What is a Pneumatic Air Cylinder

A pneumatic air cylinder is a device that converts compressed air energy into linear motion to perform tasks such as lifting heavy objects or operating machinery.
The main body where the piston moves is the cylinder. The component that moves inside the cylinder creates force is the piston and end caps seal the chambers and allow compressed air to enter or exit. When compressed air enters one side of the piston, it pushes the piston to the other side which creates movement for lifting, pushing, or pulling.
Pneumatic air cylinders are widely used in automotive, packaging, and robotics industries.
Why You Need To Calculate Pneumatic Air Cylinder Force?
Pneumatic air cylinders convert compressed air into mechanical force which allows them to perform tasks like pushing, pulling, or lifting. Understanding how force is generated and calculating the force of a pneumatic air cylinder is crucial for several reasons:
- Performance: Ensures the cylinder can handle the loads it will encounter.
- Safety: Prevents accidents from using improperly sized cylinders.
- Efficiency: Helps optimize the performance of the system.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Allows for better budgeting when purchasing equipment.
How to Calculate the Force of a Pneumatic Air Cylinder Using a Calculator (Step-By-Step)
To calculate the force of a pneumatic air cylinder, you can use the following formula:
The Force Formula
Force (F)= Pressure (P) × Area (A)
Where:
- F = Force in pounds (lbs)
- P = Pressure in pounds per square inch (PSI)
- A = Area in square inches (sq in)
Step 1: Gather Required Information
You need:
- Pressure (P) in PSI (pounds per square inch)
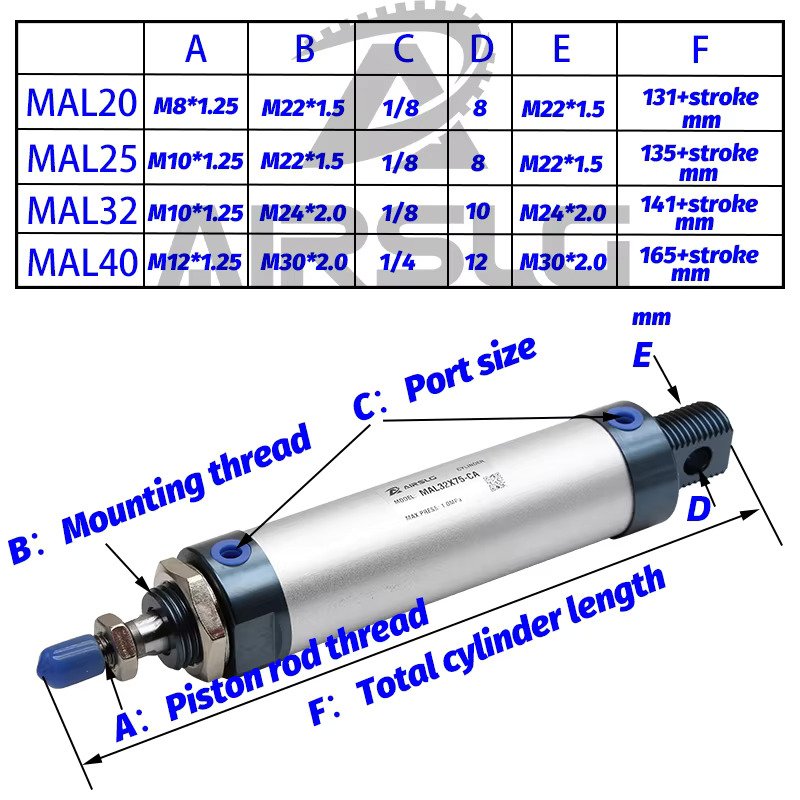
- Diameter (D) of the piston in inches.
Measure Pressure in PSI

1. Using a Pressure Gauge:
- Attach a pressure gauge to the air supply line.
- Turn on the air supply and read the pressure displayed in PSI.
2. Using an Electronic Pressure Sensor:
- Install the sensor in the system and connect it to a display device.
- Observe the reading for pressure in PSI.
3. Consult System Specifications:
- Check the equipment’s technical documentation for the expected pressure.
Measure the Diameter of the Piston in Inches

1. Using a Caliper:
- Open the caliper and place it around the piston.
- Close it until it fits snugly, then read the measurement in inches.
2. Using a Ruler or Tape Measure:
- Measure the widest part of the piston from one side to the other.
- Convert the measurement to inches if needed.
3. Referencing Manufacturer Specifications:
- Check the product specifications provided by the manufacturer for the piston diameter
Step 2: Calculate the Area (A)

To find the area of the piston, use the formula for the area of a circle:
A = πr2
This formula looks complicated, but it’s simple when you break it down:
- Measure the diameter (D) of the piston in inches.
- Divide the diameter by 2 to get the radius. Example: If the diameter is 4 inches, enter 4 ÷ 2 = 2
- Square the radius (multiply the radius by itself), Enter 2 × 2 = 4
- Multiply by Pi (3.14), Enter 4 × 3.14 = 12.56
Here we got A(area) = 12.56
Step 3: Input Pressure
Let’s take,
Pressure (P) = 80 PSI (as an example)
Step 4: Calculate the Force (F)
After getting the P(pressure) and A(area) we can easily find F(force)
Now use the force formula:
F= (P×A)
Using a Calculator:
Here we got,
- P = 80 PSI
- A = 12.56
Now, multiply the Pressure by Area:
F = (P×A)
F = (80 × 12.56)
F = 1004.8 pounds
Thus, the force generated by this pneumatic air cylinder is approximately 1004.8 pounds.
Summary of Steps to Calculate Pneumatic Air Cylinder Force
- Force calculation equation: F = P × A
- Measure the pressure (P): Get the pressure in PSI.
- Measure the diameter (D): Find the diameter of the piston in inches.
- Calculate the radius: Divide the diameter by 2.
- Find the area (A): Use A = π × (radius)2
- Calculate the force (F): Multiply pressure by area.
Key Considerations for Pneumatic Air Cylinder Force Calculation
- The size of the piston matters. A bigger piston means more force.
- Measure how much air pressure (in PSI) is being used. Make sure it’s within safe limits for the cylinder.
- Know if your cylinder is single-acting (works on one side) or double-acting (works on both sides).
- Consider how fast the cylinder moves. Speed can change how well it works.
- The air’s temperature and moisture level can change pressure readings. Keep the air clean and dry.
- How you mount the cylinder (horizontal or vertical) can affect its performance.
- Ensure the calculated force is strong enough to move the intended load.
- Always add a little extra force as a safety measure to prevent failures.
Conclusion
Calculating the force of a pneumatic air cylinder is a vital step in ensuring its efficiency and effectiveness in various applications. By understanding the key factors involved—such as piston diameter, air pressure, and cylinder type—you can make informed decisions that enhance the performance of your pneumatic system.
While online calculators are useful for quick estimates, they may not always provide accurate results due to varying conditions and input errors. It’s best to use them as a starting point and consider manual calculations or expert advice for important applications. This approach will help you optimize your pneumatic system for reliability and performance.