This perfect air intake is crucial for good engine performance. It helps the engine run smoother, use less fuel, and even have more power when you need it. So, the VVT is like a tiny air traffic controller for the engine, making sure it gets the right amount of air for optimal performance.
What is a Variable Valve Timing Solenoid (VVT)?
Your car engine needs air to run, but it needs the right amount at the right time. The variable valve timing solenoid (VVT) is a small but important part that controls this. It works like a switch that opens and closes based on signals from the car’s computer.
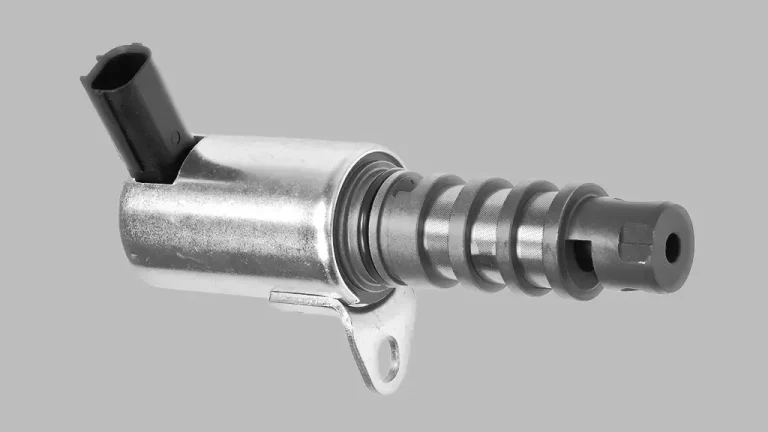

Imagine the engine has air vents, like the ones in your house. The VVT controls when these vents open and close. By carefully timing when these vents open and shut, the VVT ensures the engine gets the exact amount of air it needs.
How Does A Variable Valve Timing Solenoid Work?
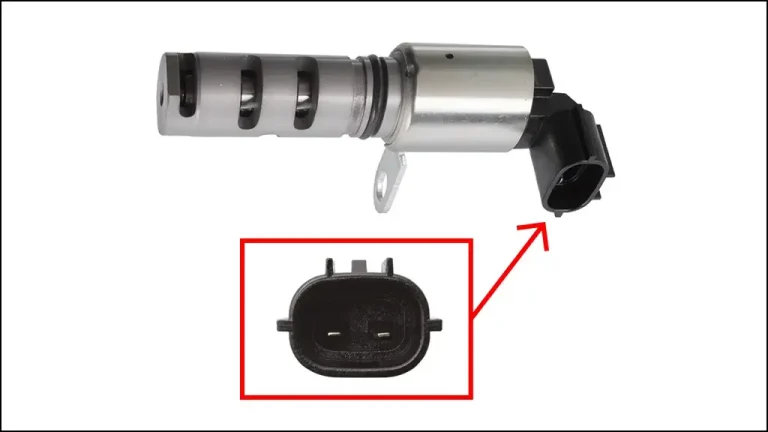

- The VVT solenoid is like a switch that controls the engine oil.
- It gets instructions from the car’s computer (ECU).
- Based on those instructions, it opens or closes a passage for the oil.
- This passage leads to a part on the camshaft (called a phaser) that controls the timing of the engine valves.
- By controlling the oil flow, the solenoid can adjust when the valves open and close.
This adjustment helps the engine run better and use less fuel.
Signs of a Bad Variable Valve Timing Solenoid (VVT)
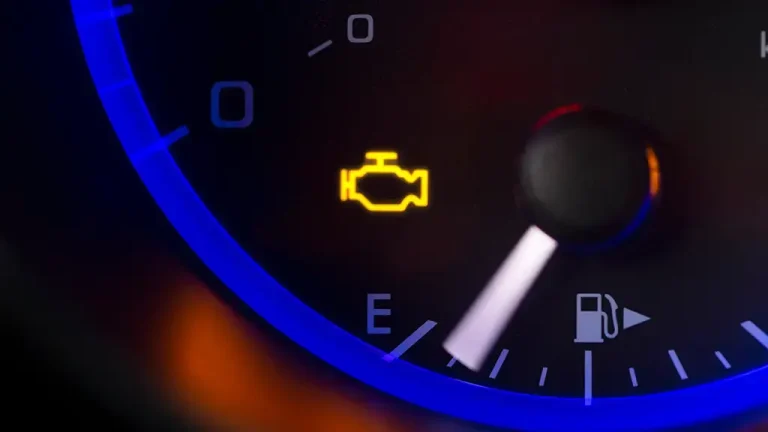

A VVT solenoid is a small but important part in your car engine. It controls when the engine valves open and close, affecting how the engine runs.
Here are some signs that your VVT solenoid might be failing:
Check Engine Light: Most modern cars will warn you with a check engine light if they detect a problem with the VVT system. This light is like a dashboard warning sign, telling you there’s an issue.
Rough Idling: If your engine feels shaky or vibrates more than usual when idling (stopped but engine running), it could be a VVT problem.
Poor Gas Mileage: The VVT system helps optimize fuel efficiency. If it’s not working right, your car might use more gas than usual.
Decreased Engine Power: A failing VVT solenoid can affect how much power your engine produces. You might notice the car feels sluggish or struggles to accelerate.
How To Install A Variable Valve Timing Solenoid?
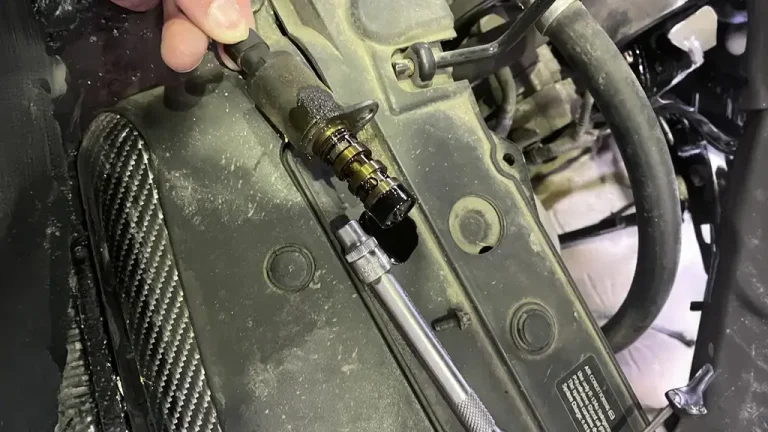

This is a basic guide to test your VVT solenoid. It’s recommended to consult a mechanic if you’re unsure about any steps.
Tools
- Multimeter
- Socket wrench or wrench set (depending on your car)
The purge valve solenoid is a part that controls fuel vapors in your car. If it’s broken, you might need to replace it.
Here’s a general guide, but remember the exact steps might differ depending on your car model:
- Find the purge valve solenoid. It’s usually near the fuel tank or engine. Check your car’s manual for its exact location.
- Safety first! Disconnect the car battery to avoid electrical issues while working.
- Locate the electrical connector plugged into the purge valve solenoid and disconnect it carefully.
- Look for bolts or fasteners holding the solenoid in place. Unscrew or unclip them carefully.
- Once loose, gently remove the old solenoid from its mounting spot.
- Take your new solenoid and put it back in the same spot. Reverse the steps you took to remove the old one: fasten it securely, reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the car battery and start the engine. This tests the new solenoid.
FAQs
Bad VVT Solenoid & No Start
Q: Can a bad VVT solenoid prevent the engine from starting?
A: A bad VVT solenoid might cause starting problems, but it’s not the most common reason. The engine computer (ECU) can usually adjust for a faulty solenoid to some degree and still allow the engine to start.
Here’s why a bad VVT solenoid might cause a no-start situation:
The VVT system helps optimize engine performance. If it’s malfunctioning, the air-fuel mixture might be thrown off significantly, making it difficult to start.
However, there are other more likely reasons for a no-start condition. It’s always best to consult a mechanic for proper diagnosis.
Replacing a Purge Valve Solenoid (Simplified)
Replacing a purge valve solenoid is a repair best left to someone comfortable working on cars. But here’s a simplified breakdown:
Find the Solenoid: It’s usually near the fuel tank or engine (check your car’s manual).
Safety First! Disconnect the car battery to avoid electrical issues.
Disconnect the Parts: Locate the electrical connector plugged into the solenoid and disconnect it carefully. There might also be bolts or fasteners holding the solenoid in place – unscrew or unclip them.
Remove and Replace: Gently remove the old solenoid and put the new one in its place. Reverse the steps you took to remove the old one: fasten it securely and reconnect the electrical connector.
Reconnect and Test: Reconnect the car battery and try starting the engine to see if the new solenoid works.
Remember, this is a general guide. Specific steps might vary depending on your car model. If you’re unsure about anything, consult a mechanic’s manual or seek professional help.