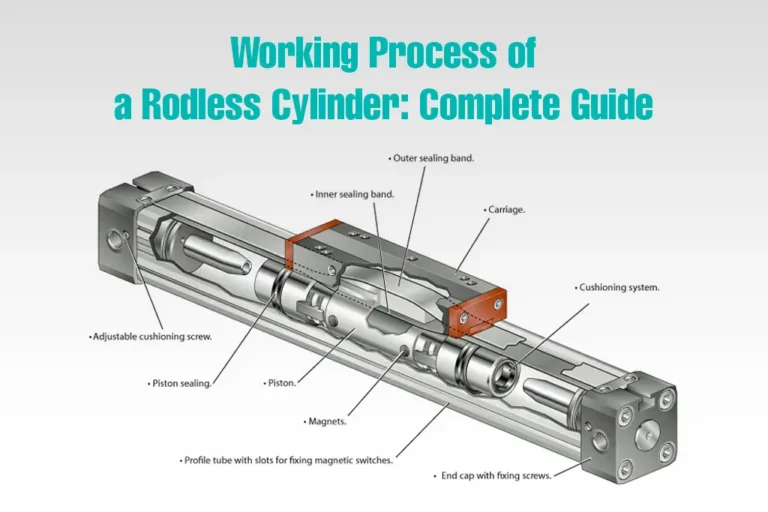
A rodless cylinder is a type of pneumatic cylinder that operates without an external piston rod. Instead, it has an internal piston mechanism that moves along the length of the cylinder body, with the load attached directly to the cylinder.
In this article, you will learn how does a rodless cylinder work and how you can select the right rodless cylinder for your application.
Different Types of Rodless Cylinder
There are several types of rodless cylinders used across many industries. Slotted-type Rodless Cylinder, Magnetic Cylinder, Magnetically Coupled Rodless Cylinder and Cable Rodless Cylinder. A Slotted-Type Rodless Cylinder is more specialized in terms of its function and value.
1. Slotted-Type Rodless Cylinder
A Slotted-Type Rodless Cylinder features a slot running along its length. This slot allows the internal piston to be connected to an external carriage, which moves along the external surface of the cylinder. The design enables the cylinder to achieve linear motion without an extending piston rod, making it highly suitable for applications with limited space.
2. Magnetic Rodless Cylinder
A Magnetic Rodless Cylinder is a type of Pneumatic Cylinder designed to provide linear motion without the use of an external piston rod. It employs a Magnetic Coupling Mechanism to transfer the motion of the internal piston to an external carriage.
Magnetic Rodless Cylinder allows for a compact and efficient use of space which makes magnetic rodless cylinders ideal for various industrial applications where space constraints and smooth operation are crucial.
3. Magnetically Coupled Rodless Cylinder
A Magnetically Coupled Rodless Cylinder provides linear motion without the need for an External Piston Rod. It uses a Magnetic Coupling between the Internal Piston and an External Carriage to transfer the motion.
4. Cable Rodless Cylinder
A Cable Rodless Cylinder provides linear motion without an Extending Piston Rod. It uses a cable system to transfer the motion of the Internal Piston to an External Carriage. This design is highly space-efficient and ideal for applications requiring long stroke lengths in confined spaces.
How Does a Rodless Cylinder Work? (Explained)
A Rodless Cylinder works by providing linear motion without the need for an Extending Piston Rod. A Rodless Cylinder uses compressed air to move an Internal Piston, which in turn moves an External Carriage along the Cylinder’s length.
Here’s a simplified explanation of how Does a Rodless Cylinder works.
1. Internal Piston Movement
There is an Internal Piston inside the Sealed Cylinder that moves back and forth when compressed air is applied to either side of it. The application of Air Pressure moves the Piston in a linear direction.
2. Connecting the Piston to the Carriage
The piston inside the cylinder is connected to the carriage outside in one of these ways:
- Slot: There is a slot in the cylinder with a seal to prevent air from escaping. The piston is linked to the carriage through this slot.
- Magnets: Strong magnets on the piston and the carriage can pull the carriage along as the piston moves.
- Cable: A cable attached to the piston inside and the carriage outside can pull the carriage along as the piston moves.
3. External Carriage
The external carriage, which is mounted on the outside of the cylinder, moves along the length of the cylinder as the internal piston moves. The carriage is directly or indirectly connected to the internal piston.
4. Moving the Carriage
When air pressure pushes the piston back and forth, the piston moves the carriage along the cylinder. This external carriage carries the load or object you need to move.
5. Sealed Environment
The cylinder is sealed to maintain air pressure and prevent contaminants from entering. This ensures efficient operation and longevity of the cylinder.
Pros and Cons of Using a Rodless Cylinder
Using a rodless cylinder has many advantages for your application but it also comes up with some limitations.
Here are some pros and cons you can keep in mind:
Pros:
- Compact design with no need for extra space for an extending rod.
- Accurate and smooth motion for precise tasks.
- Carries larger and heavier loads efficiently.
- Mounted in various positions and orientations.
- Uses air efficiently, reducing friction and costs.
Cons:
- Initially more Expensive than Traditional Cylinders.
- Installation and Repairs can be more complicated.
- May not Push or Pull as strongly as Rod Cylinders.
- Not all sizes and types are easy to find.
- Extreme Temperatures can affect performance.
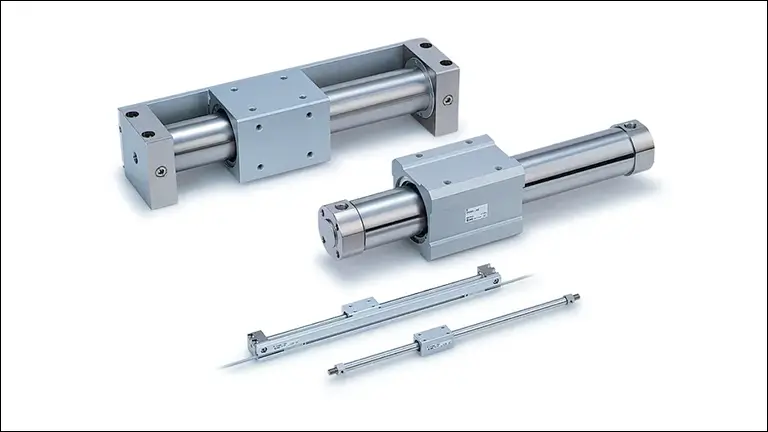

Things To Consider While Choosing a Rodless Cylinder
Piston Stroke Length: This is how far the cylinder can move back and forth. Make sure it’s long enough for your needs.
Load Capacity: Consider how much weight the cylinder can handle. If you’re lifting something heavy, you’ll need a cylinder that’s strong enough.
Speed: Some cylinders are quicker than others, so choose one that matches your speed requirements.
Mounting Options: Check how you can attach the cylinder to your machine or equipment. Different cylinders have different mounting options, so make sure it fits.
Space: Rodless cylinders can save space because they don’t have a rod sticking out. Think about how much room you have for the cylinder to move.
Seals and Protection: Look for cylinders with good seals to keep out dust and dirt. This helps the cylinder last longer and work better.
Maintenance: Consider how easy it is to maintain the cylinder. Some might need more upkeep than others, so think about what you can handle.
Budget: Lastly, think about your budget. Rodless cylinders come in different price ranges, so find one that fits your budget while still meeting your needs.

Where Rodless Cylinders Are Commonly Used
Rodless cylinders are used in various industries where precise and space-efficient linear motion is needed, such as:
Manufacturing: For moving parts along a production line.
Packaging: For handling packages in automated systems.
Automotive: For positioning parts during assembly.
Medical Devices: For moving components in clean, controlled environments.
Robotics: For providing precise motion in robotic arms and other automated systems.
Conclusion
Rodless cylinders provide a versatile and efficient solution for linear motion applications. Their compact design, long stroke capabilities, smooth and precise movement, and reduced maintenance make them a valuable component in many industrial and commercial settings. By offering space efficiency, high load capacity, and energy savings, rodless cylinders are an excellent choice for optimizing performance in various applications.