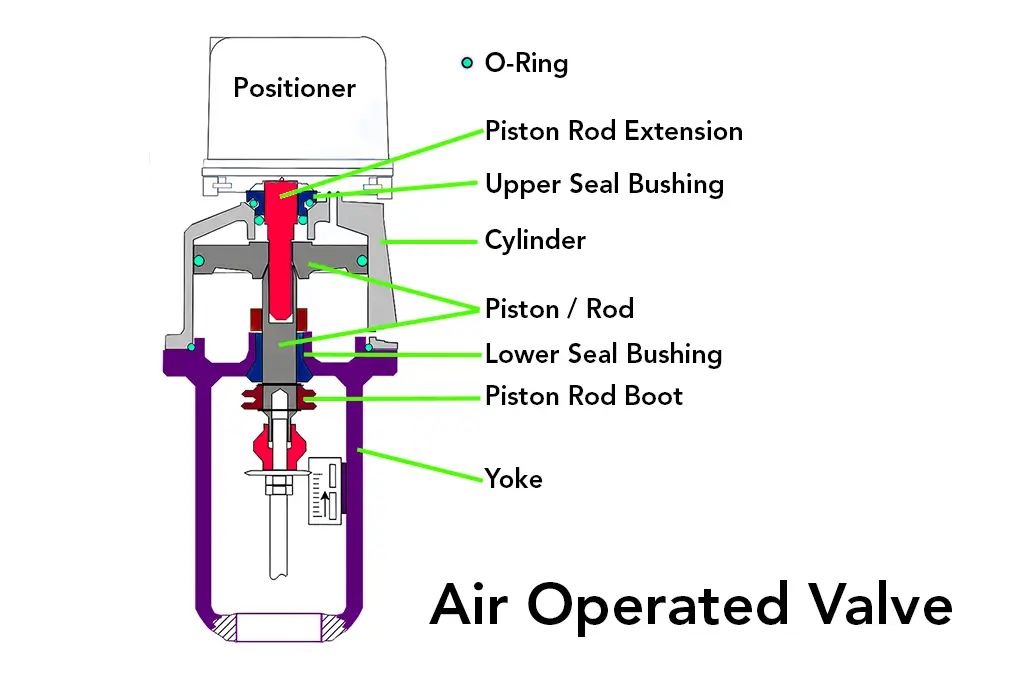
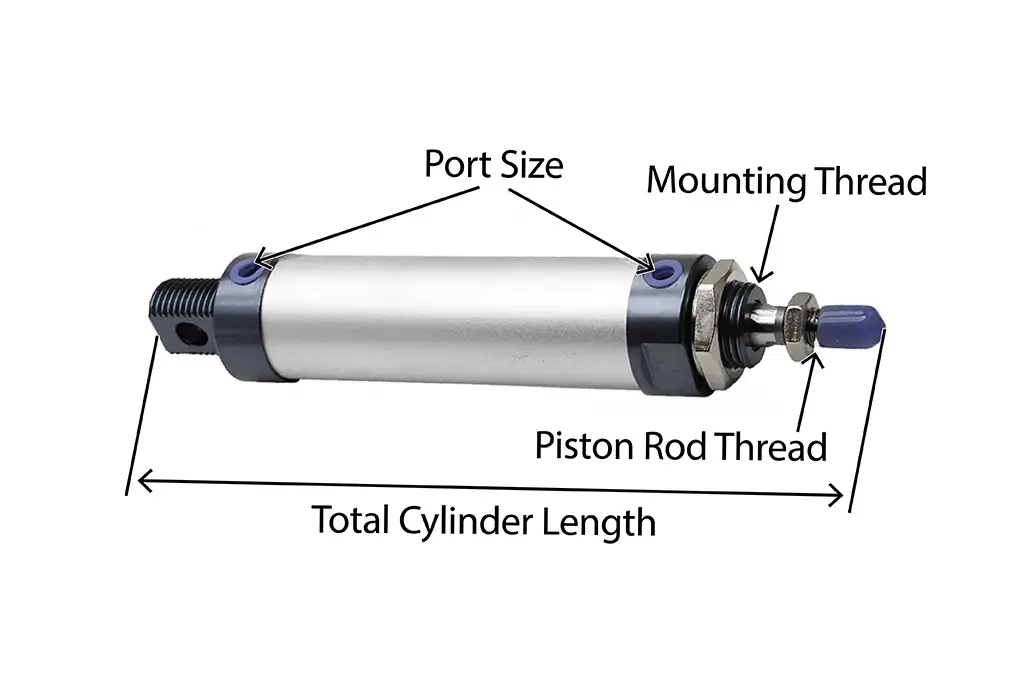
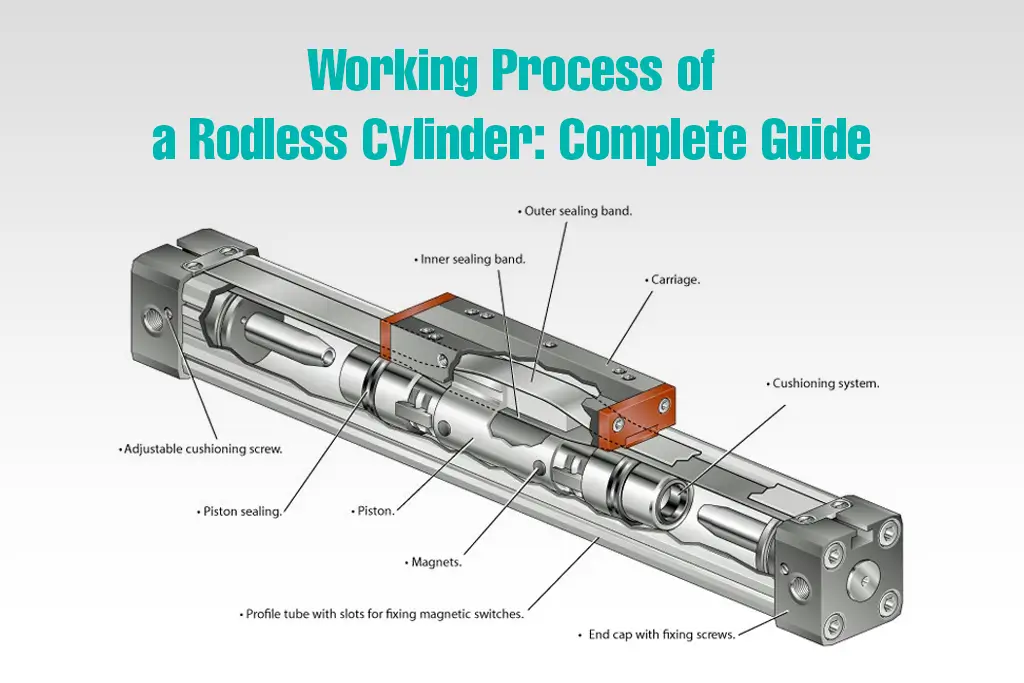
Directional control valves are some of the most vital valves in the industry. They are used in directing air flow, liquids, and hydraulic fluids within machines to ensure all operations run well and effectively. This blog will highlight what is a direction control valve, how they operate, and why they are valuable.
What is a Direction Control Valve?
The direction control valve refers to a device that directs the flow of fluid or air in a system. It decides where the fluid (such as hydraulic oil or compressed air) goes and how it gets there. Just as a traffic controller helps traffic move in the right direction at the right time, a directional control valve does so for fluids.
Directional control valves are widely used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. including machinery such as forklifts, factory automation equipment, and even airplanes.
How Does a Direction Control Valve Work?
The valve works by opening and closing internal passages to control the flow of fluid or air. It has several ports (openings) where fluid enters and exits. By shifting the valve’s internal parts, it can:
- Stop the flow.
- Allow the flow to continue in one direction.
- Redirect the flow to another path.
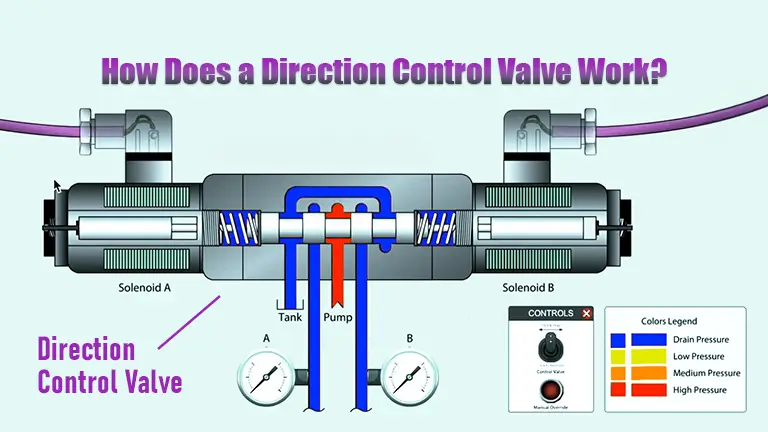
The hydraulic directional control valve is used in systems that rely on pressurized liquids, while an air directional control valve is used in systems powered by compressed air. Both types function similarly but are designed for different mediums.
Types of Direction Control Valves
There are several kinds of directional control valves, each for specific tasks. Below are some common ones:
Hydraulic Directional Control Valves
These directional hydraulic control valves are used in hydraulic systems where liquids serve as the working fluid. They are commonly used in heavy construction equipment, such as excavators, which ultimately drive arms and buckets.

Pneumatic Directional Control Valves
These valves are designed for systems that use compressed air. You’ll see these in industries like packaging or food processing, where quick and precise movements are required.

Manual, Solenoid, and Pilot-Operated Valves
- Manual valves require a person to operate them, often with a lever.
- Solenoid valves are controlled electronically, making them common in automated systems.
- Pilot-operated valves use another fluid (like air or hydraulic oil) to control the main valve.

Why Are Direction Control Valves Important?
- Efficiency: Direction control valves enable machinery to work faster and more efficiently due to the proper flow of fluids or air.
- Precision: They allow for accurate control, which is vital in industries like manufacturing.
- Safety: They help prevent malfunctions or accidents that may result from fluid leakage or improper flow.
Choosing the Correct Directional Control Valve
Selection of a Direction Control Valve Depends On:
- System Type: hydraulic or pneumatic.
- Flow Capacity: amount of fluid or air to be allowed.
- Control Method: manual, solenoid, or pilot-operated.
- Environment: Will the valve be exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, or dirt?
Conclusion
A valve directional control is a crucial element within hydraulic and pneumatic systems, as it ensures that the movement of fluids or air is in a correct manner so that the machines work efficiently and safely.
Whether you need a hydraulic directional control valve for heavy machinery or an air directional control valve for industrial automation, the right choice of a valve is critical for seamless operations.