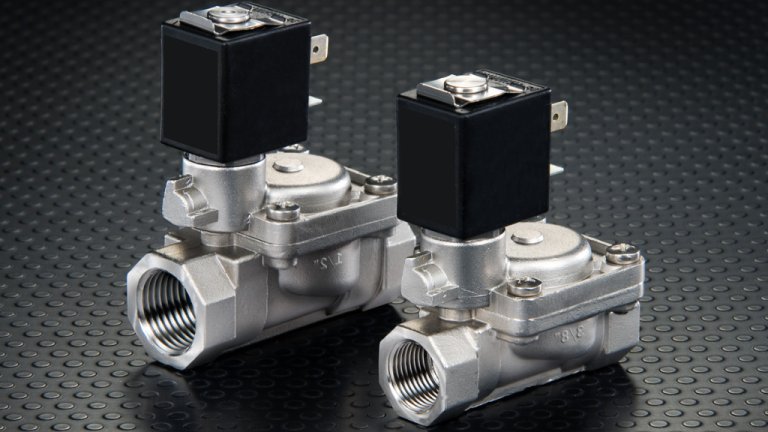
Solenoid valves are remote-controlled gatekeepers for fluids. They use an electromagnet, called a solenoid, to manipulate a metal plunger. When electricity flows through the coil, it magnetizes it, attracting the plunger. This movement opens or closes internal passages in the valve body, controlling the flow of liquids or gases. With a spring pushing the plunger in the opposite direction, solenoid valves come in two types: normally open (spring keeps it open until activated) and normally closed (spring keeps it shut until activated). These versatile valves are used in everything from car engines to irrigation systems.
What is a solenoid valve?
A solenoid valve is a type of electromechanical device used to control the flow of fluids such as air, water, gas, steam, or other liquids. It consists of a coil of wire (solenoid) wound around a metal core, which generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. This magnetic field causes a plunger or armature to move within the valve body, either opening or closing a passage for fluid flow.
This guide provides comprehensive insight into solenoid valves, detailing their operational principles and offering clear guidelines for understanding their functionality.
How does a solenoid valve work?
A solenoid valve operates by utilizing an electromagnetic mechanism to regulate the flow of fluid through a passage. It comprises essential components such as a solenoid coil, plunger, valve body, ports, and a valve seat.
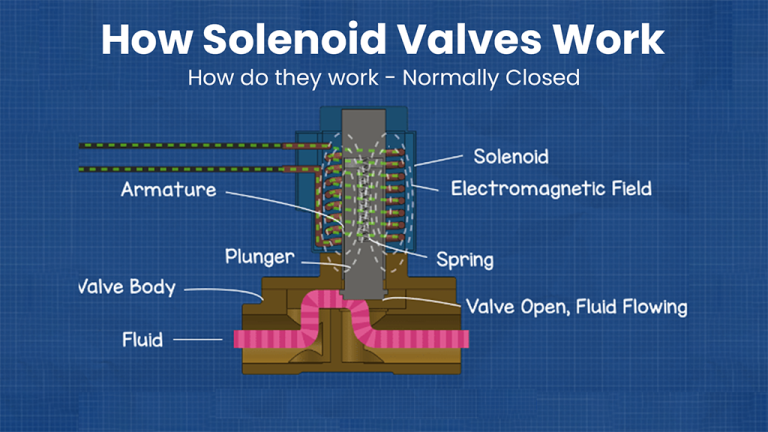
When an electrical current passes through the solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field that moves the plunger. This movement either opens or closes the valve, controlling the flow of fluid. Depending on its configuration (normally closed or normally open), the valve either allows fluid to flow or blocks it.
The picture here shows how a solenoid valve actually works using its components.
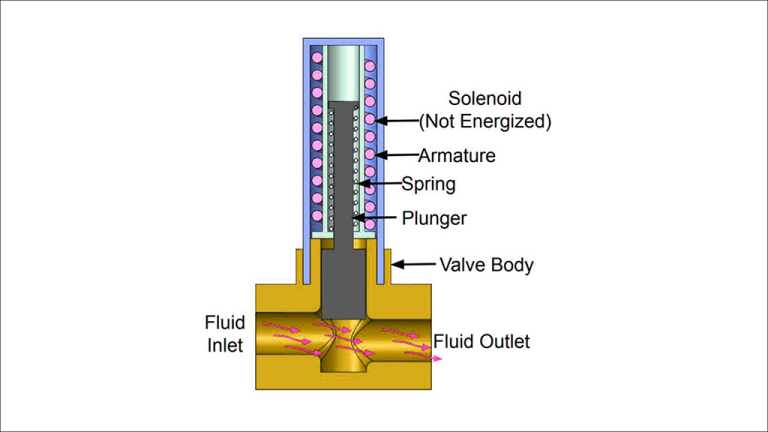
- Solenoid Coil: This coil, typically made of wire wrapped around a metal core, acts like a mini electromagnet. When electricity flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field.
- Plunger: This metal rod moves up and down within the Valve body. It’s connected to a disc or seal that functions like a gate, controlling the flow path.
- Valve Body: This is the housing that contains all the components and channels for the fluid to travel through. It also has an opening called the orifice, which is the point of control.
- Spring: A hidden helper, the spring pushes the plunger in a specific direction (usually closed) when there’s no electrical signal.
Let’s take a normally closed (NC) solenoid valve as an example:
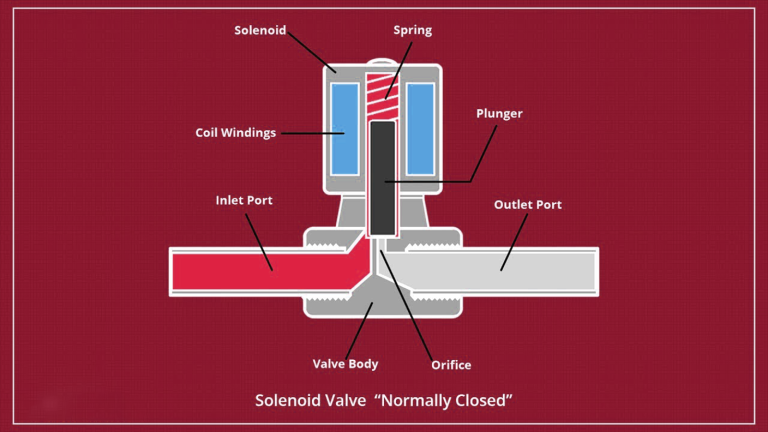
When there’s no electrical current, the coil isn’t energized. The spring takes charge, pushing the plunger down. This action forces the seal on the plunger to block the space in the valve body, essentially closing the gate and stopping any fluid flow.
When electricity is applied to the coil, it becomes a mini magnet. This magnetic field pulls the plunger upwards against the spring’s force.
As the plunger rises, it lifts the seal away from the orifice. This creates a clear pathway for the fluid to flow through the valve, opening the gate.
Once the electrical signal ceases, the magnetic field disappears. The spring regains control, pushing the plunger back down. This closes the seal on the space once again, stopping the flow of fluid.
By using electricity to control fluid flow electronically, it offers a simple and efficient solution for various applications. Their compact size, reliability, and versatility make them a valuable component in modern technology.
The Working Principles Of Solenoid Valve
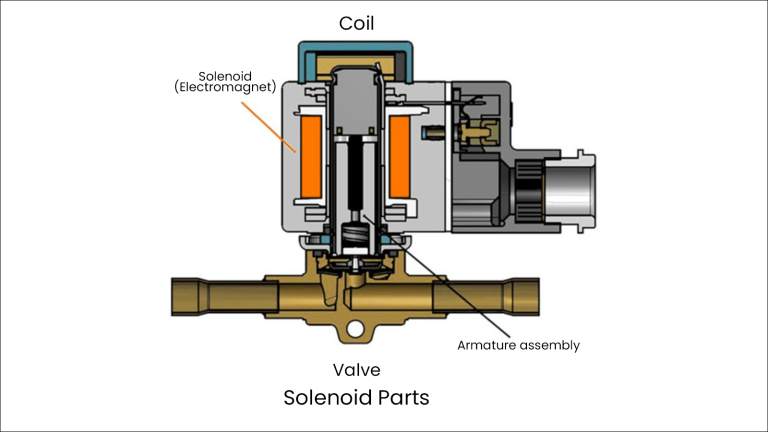
Solenoid valves have two main parts, the solenoid and the valve itself. The valve has openings, while the solenoid contains a coil, sleeve assembly, and plunger.
When you send electricity through the coil, it creates a magnetic field. This field moves the plunger up or down, which opens or closes the valve’s openings. This action controls the flow of gas or liquid, like turning a faucet on or off.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Solenoid Valve
Solenoid valves are great because they serve multiple purposes in many industries. They’re good for handling liquids or gases, and they are quite efficient because they don’t need a lot of wiring or money to set up.
Advantages
- Quick and precise control of fluid or gas flow.
- Compact design, easy to install and integrate.
- Rapid response time, suitable for automated systems.
- Cost-effective compared to other valve types.
- Versatile, suitable for various industries and applications.
Disadvantages
- Susceptible to contamination, affecting performance.
- Sensitive to voltage fluctuations, may malfunction.
- Limited pressure and temperature range.
- Reliability concerns in harsh environments.
- Maintenance and repair may require specialized knowledge.
What Types of Valves Are Used in Solenoid?
There are 3 types of valves that offer versatility and flexibility in various applications, allowing for precise control of fluid flow in different systems.
Two-way Solenoid
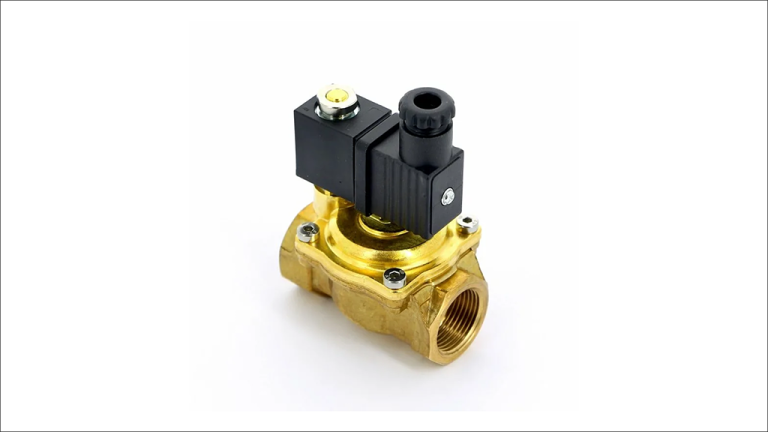

Two-way solenoid valves are commonly used for on/off control. These valves have two ports. One port is for allowing the fluid to flow in one direction when the valve is energized, and another port is for blocking flow when de-energized.
Three-way Solenoid Valve

Three-way solenoid valves are a type of solenoid valve with three ports. One inlet and two outlets. They are commonly used to control the flow of fluid between two different paths or to mix fluids from two different sources.
Four-way Solenoid Valve
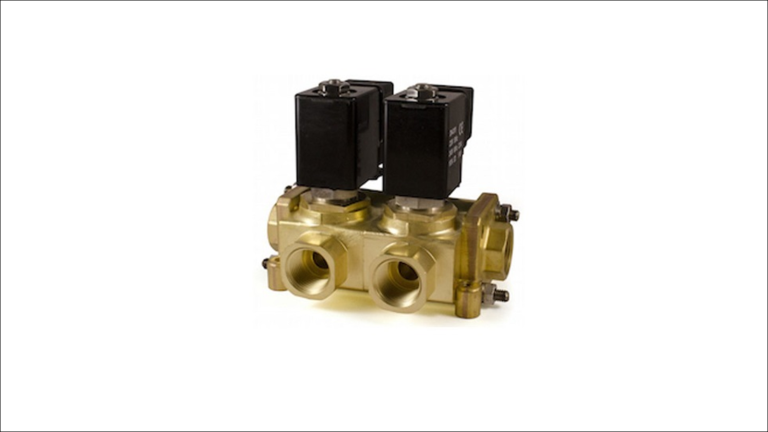

Four-way solenoid valves are a type of solenoid valve with four ports: two inlet ports and two outlet ports. They are commonly used in pneumatic and hydraulic systems to control the flow of pressurized air or fluid and to switch between different circuits or actuate double-acting cylinders.
Different Types Of Solenoid Valve
There are 3 types of Solenoid Valves
- Normally closed Solenoid Valve
- Normally open Solenoid Valve
- Bi – stable Solenoid Valve
Normally closed Solenoid Valve
A Normally Closed (NC) Solenoid Valve is a type of valve that remains closed in its default state, without any electrical power applied to the solenoid. When an electrical current is applied to the solenoid, it generates a magnetic field that lifts the valve’s plunger, allowing fluid to flow through the valve. Once the electrical current is removed, the solenoid de-energizes, and the valve returns to its closed position, stopping the flow of fluid.
Normally open Solenoid Valve
A Normally Open (NO) Solenoid Valve is a type of valve that remains open in its default state, without any electrical power applied to the solenoid.
When an electrical current is applied to the solenoid, it generates a magnetic field that pulls the valve’s plunger, closing the valve and stopping the flow of fluid. Once the electrical current is removed, the solenoid de-energizes, and the valve returns to its open position, allowing fluid to flow again.
Bi-stable Solenoid Valve
A bi-stable A solenoid valve is a type of Solenoid Valve that has two stable states or positions, hence the term “bi-stable.”
Unlike traditional solenoid valves that require continuous power to maintain either an open or closed position, bi-stable solenoid valves only require a brief pulse of electrical current to switch between their two stable states. Once switched, they maintain their position without the need for continuous power.
Direct, Indirect & Semi-Direct Acting Solenoid valves
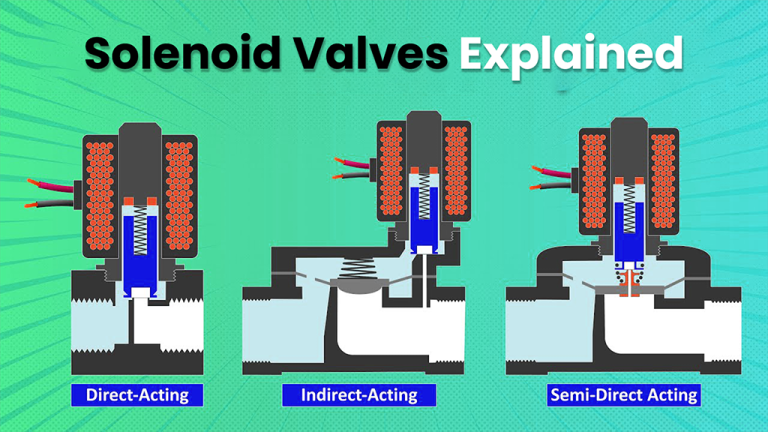
Direct Acting Solenoid Valves directly control the opening and closing of the Valve seat. When energized, the Solenoid lifts the plunger, allowing fluid to flow through. They are suitable for low flow rates and pressure differentials. Direct acting Solenoid Valves are known for their simplicity and fast response times.
Indirect Acting Solenoid Valves use the solenoid to control a pilot valve, which regulates the flow of fluid through the main valve. When energized, the solenoid opens the pilot valve, allowing pressure to close the main valve. They are preferred for applications with higher flow rates and pressure differentials. Indirect acting solenoid valves can handle higher pressures without requiring a larger solenoid.
Semi-direct Acting Solenoid Valves combine features of both direct and indirect acting valves. They have a small pilot orifice allowing some fluid to flow directly through the Main Valve. The majority of fluid flow is controlled indirectly through a Pilot Valve. Semi-direct Acting Solenoid Valves offer a balance between response time and pressure handling capabilities. They are commonly used in applications with moderate flow rates and pressure differentials.
Where are solenoid valves used?

Solenoid valves are used in a wide range of industries and applications due to their versatility and effectiveness in controlling fluid flow. Some common areas where it is used include:
- Industrial Automation
- Water and Wastewater Treatment
- Heating, Ventilation, & Air Conditioning Systems
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment
- Automotive Industry
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Food and Beverage Processing
- Agricultural Applications
- Fire Protection Systems
- Household Appliances
Choosing The Right Solenoid Valve For Your Components
Selecting the right Solenoid Valve involves thorough consideration of various factors to ensure it aligns with the specific requirements of the application. This includes assessing fluid compatibility, flow rate, pressure, size, and connection type. Additionally, factors such as operating environment, electrical specifications, response time, certifications, and budget constraints play crucial roles in the selection process.
By carefully evaluating these criteria, you can ensure the respective solenoid valve meets the specific requirements of your application, providing optimal performance and reliability.
You can find a variety of solenoid valves from Maxim Systems from top leading manufacturers. Visit Maxim Systems today for assistance in selecting the right valve for your application.
1. What is a solenoid valve, and what is its primary function?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device used to control the flow of fluid in a system. Its primary function is to open or close the valve based on the application of an electrical current to the Solenoid coil.
2. How does a solenoid valve differ from other types of valves?
Unlike traditional valves that rely on manual operation or mechanical mechanisms, solenoid valves use an electromagnetic mechanism to control fluid flow, offering precise and rapid response capabilities.
3. What are the common applications of solenoid valves in everyday life?
Solenoid valves are commonly used in various applications, including dishwashers, washing machines, irrigation systems, automotive engines, HVAC systems, and industrial machinery.
4. What are the main components of a solenoid valve, and how do they function together?
The main components of a solenoid valve include a Solenoid Coil, Plunger or Armature, Valve body, Ports, and a Valve seat. These components work together to control the opening and closing of the valve in response to electrical signals.
5. How does the electromagnetic mechanism in a solenoid valve work to control fluid flow?
When an electrical current is applied to the solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field that moves the plunger or armature, thereby opening or closing the valve and controlling the flow of fluid through the system.
6. What factors should be considered when selecting a solenoid valve for a specific application?
Factors to consider include the type of fluid, flow rate, pressure, temperature, voltage, response time, material compatibility, and certifications required for the application.
7. What are some signs of a malfunctioning solenoid valve, and how can they be addressed?
Signs of a malfunctioning solenoid valve include failure to open or close, partial opening, unusual noises, or coil damage. Troubleshooting steps may involve checking electrical connections, cleaning or replacing components, or consulting a professional for repair or replacement.
8. Are there different types of solenoid valves available, and how do they differ in operation?
Yes, there are different types of solenoid valves, including direct acting, indirect acting, and pilot-operated Valves. These types differ in how they control fluid flow and the mechanism used to actuate the Valve.
9. Can solenoid valves be used in hazardous environments or with corrosive fluids?
Yes, solenoid valves are available in various materials and configurations to withstand harsh environments and corrosive fluids. It’s essential to select a valve with appropriate specifications for the specific application.
10. What maintenance procedures are recommended to ensure the proper functioning of solenoid valves over time?
Regular maintenance may include cleaning or replacing filters, inspecting electrical connections, lubricating moving parts, and testing valve performance to ensure optimal operation and longevity.