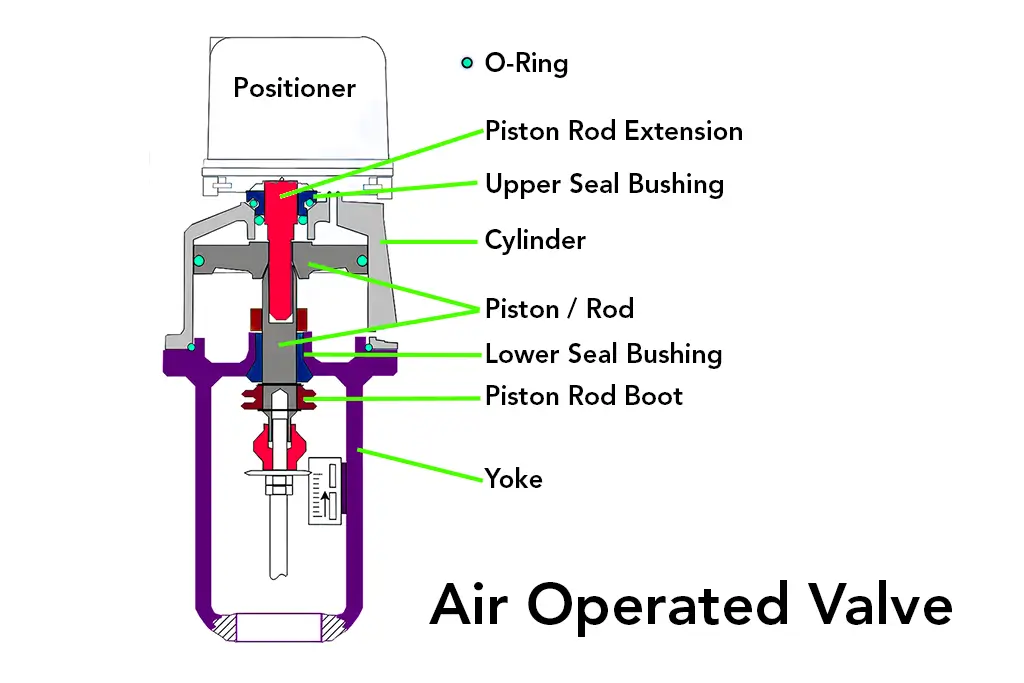
An air-operated valve, also known as a pneumatic valve, plays an important role in industries where the flow of any fluid or gas needs to be controlled. These valves are widely used in applications like manufacturing and chemical processing, among other fields. But how does an air-operated valve work? In this blog, we’ll break it down to a simple explanation of its operation mechanism, the need, and why they are important.
What is an Air Operated Valve?
The air-operated valve, sometimes called the pneumatically operated valve, is one that uses compressed air for operation-opening, completely shutting, or regulating liquids or gases in a pipeline. As opposed to a manual valve, which would require physical energy, these air operated valves depend on pneumatic energy, hence making them more effective and efficient in a number of uses when applied industrially.
They are ideal for operations that require being remotely operated, high-pressure systems, and those places where both precision and speed are needed. Based on the design and application, these valves can be used either for on/off control or for modulating flow.
How Does an Air-Operated Valve Work: Step-By-Step
To understand how does an air operated valve work, let’s break it down step by step:
The Role of Compressed Air
The Major Source in the running of air operated valves is compressed air. Compressed air is supplied thru a pneumatic system down to the valve’s actuator. The actuator is that part of the valve responsible for converting pneumatic energy to mechanical motion.
The Actuator
The actuator is considered the heart of the air-operated valve, as it decides whether the valve should open, close, or stay in a partially open position. Two major types of actuators that may be used in air-operated valves are as follows:
- Single-Acting Actuators: This actuator uses air pressure in order to move the valve in one direction such as open or close and relies on a spring to return to its original position.
- Double-Acting Actuators: These pneumatically actuate the valve in both directions, requiring no spring.
Valve Operation
The action of the valve is described based on the actuator type and design of the valve. Here’s a basic explanation of how that process works:
- Compressed air enters the actuator through an inlet port.
- The air pressure creates force and begins to move a piston/diaphragm inside the actuator.
- This movement is converted to a mechanical motion which will either elevate or will rotate some internal parts of the valve, such as plug, disc, or ball.
- These moving internal parts will regulate the flow of fluid or gas through the valve.
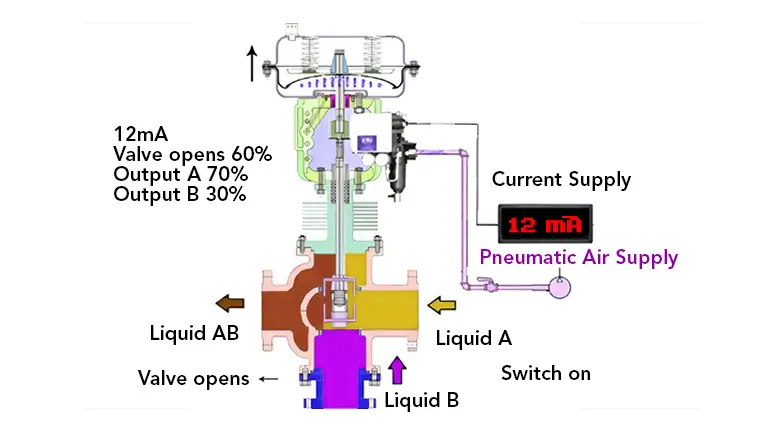
Types of Air Operated Valves
There are several types of air-operated valves available, each designed for different applications. They include:
1. Air Operated Ball Valves
These types of valves use a ball with a hole in the middle. The actuator rotates the ball. It either aligns the hole with the pipeline for flow or blocks it to stop the flow.
2. Air-Operated Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves use a rotating disc to regulate flow. They are lightweight, compact, and ideal for large-diameter pipelines.
3. Air-Operated Diaphragm Valves
These valves are equipped with a flexible diaphragm that travels up or down depending on the flow of fluids. They serve well in handling corrosive or viscous fluids.
4. Air-Operated Globe Valves
Globe valves have a linear motion design, hence are suitable for applications involving precise flow regulation.
Find the details and wide range of air operated valves on MaximSystems.
How To Choose the Right Air Operated Valve
The proper selection of the appropriate air-operated valve in an application would take due regard for the following considerations:
- Ensure the pressure and temperature of your system can be supported by the valve.
- The materials used to make the valve will be compatible with the fluid or gas handled.
- Decide the type of actuator whether the operation requires single-acting or double-acting actuators.
- Identify a valve whose size coincides with the pipeline and at the same time can achieve the desired flow rate.
- Choose valves that have little maintenance and serve for long periods
Advantages of Air Operated Valves
There are numerous advantages offered by air-operated valves, which make them popular in industries:
1. High Efficiency
Pneumatic systems move at incredible speed, hence ensuring opening and shutting of the valves very fast.
2. Safe Operations
Since these kinds of valves use compressed air instead of electricity or human effort, they are safe to handle in hazardous conditions.
3. Remote Control
Air-operated valves have the option for remote operation. Thus, operators may be located at a safer distance when operating systems.
4. Flexibility
Compatible with many types of fluids and gases in a wide operating range of conditions, making them adaptable to many industry needs.
5. Little Maintenance
With fewer moving parts compared to other valve types, air-operated valves require less maintenance, therefore reducing downtime and costs.
Conclusion
So, how does an air-operated valve work? Well, essentially, it regulates the flow of liquids or gases through a pipeline using compressed air. The actuator converts air pressure to mechanical motion that allows a valve to open, shut, or adjust the flow of a medium.
From water treatment and manufacturing, among many industries, air-operated valves are versatile, efficient, and reliable. Having explained the working mechanism, the types, and applications of air-operated valves, you will go a long way in securing a better decision on their inclusion within your systems.
If you would like to upgrade your process in industry, air-operated valves are a sensible choice for increasing efficiency and safety.